Class EvaluationController
The Controller class for the evaluation REST interface.
Inherited Members
Namespace: Quantellia.WMServer.Execution
Assembly: WMServer.dll
Syntax
[Authorize]
[ApiController]
public class EvaluationController : ControllerBaseConstructors
EvaluationController(WMAppDbContext)
Create a new instance and inject an WMAppDbContext
Declaration
public EvaluationController(WMAppDbContext context)Parameters
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| WMAppDbContext | context |
Methods
Delete(int)
Delete the Evaluation record with the specified Id.
Declaration
[HttpDelete("evaluation/{id}")]
public void Delete(int id)Parameters
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| int | id | ID of the Evaluation record to delete. |
Evaluate(EvaluationArgs)
Performs a single evaluation against the TemporaryModel contained in this evaluation. Throws an exception if no TemporaryModel is provided. Does not save results. See Evaluate(string, EvaluationArgs) (/evaluate/{id}) for the full explanation of features.
Declaration
[HttpPost("evaluateSingle")]
public Task<ActionResult<EvaluationResult>> Evaluate(EvaluationArgs args)Parameters
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| EvaluationArgs | args |
Returns
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Task<ActionResult<EvaluationResult>> |
Evaluate(string, EvaluationArgs)
Executes or initializes a decision model.
Declaration
[HttpPost("evaluate/{id}")]
public Task<ActionResult<EvaluationResult>> Evaluate(string id, EvaluationArgs args)Parameters
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| string | id | ID of the decision model to execute. |
| EvaluationArgs | args |
Returns
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Task<ActionResult<EvaluationResult>> | The results calculated by the decision model. |
Remarks
The World Modeler execution processor is accessed via the REST API by
requesting the evaluate operation. The call syntax for this is:
[application root]/evaluate/{id}where:
| [application root] | is the root URL of the application, that is, the full URL to which / is resolved. |
| {id} | is the ID of the DecisionModel that is to be evaluated. |
{
"processorID": string, empty string, or null,
"temporaryModel": [ array of decision model element objects to evaluate ] or null,
"returnElements": [ array of strings ] or null,
"arguments": { empty object or object with name = value pairs } or null,
"saveAs"
"UserData": string or null
}| processorID | The ID of a processor which has been created by a previous call to Runand is still valid.
If this is the first time Run is being called, processorID should be null, or an empty string and the new processor ID
will be returned in the response if the call succeeded.
See Lifecycle of a processor, below.. | ||||||
| temporaryModel | A list of objects corresponding to decision model elements, or null. If null, the temporary model will be ignored. If not null then the list of elements will be compiled into a temporary decision model and evaluated, and the processorID generated will correspond to this model. Only evaluatable elements will be used. If a processorID is passed in as well, the temporaryModel will be ignored. | ||||||
| returnElementIDs | An array of strings, each of which is the ID,
FullyQualifiedName, or Name
of a DecisionModelElement in the
DecisionModel specified in the id URL arguments. Note that the search for matching elements is performed
in the order specified above.
The purpose of this is to allow the caller to limit the data that is returned when the processor evaluates the model to only those elements that the caller is interested in. This improves efficiency and reduces network traffic when large models are evaluated. The following values may be specified:
| ||||||
| arguments | A JSON object containing name = value pairs, where each name identifies an element in the
DecisionModel and instructs the processor to set the specified element to the specified value before evaluating the model.
Each model element name may be specified either by its FullyQualifiedName or
its Name. The value must satisfy the following:
For example:
Incorrect | ||||||
| saveAs | If the inputs and results of the execution are to be saved, then this arguments specifies the name used to refer to the saved execution. If this arguments is null, then the execution will not be saved. | ||||||
| summary | May be null. If the saveAs arguments is not null, then this arguments allows a short summary string
to be included in the record of the saved execution run. If saveAs is null, then this
arguments is ignored.
| ||||||
| documentation | May be null. If the saveAs arguments is not null, then this arguments allows a longer documentation
string to be included in the record of the saved execution run.The MIME type of the string
must be specified in the documentationMIMEType arguments.If saveAs is null, then this arguments is ignored. | ||||||
| documentationMIMEType | If both the saveAs arguments and the documentation
arguments are not null, then this arguments must be set to the string identifying the MIME
type of text in the documentation arguments. If either saveAs or documentation are null, then this arguments is ignored. | ||||||
| UserData | An optional, user-defined text string that can be passed with the call. If defined, thie string will be returned in the response to this call. This can be used for associating response instances with the calls they belong to, for example, to sort the sequence of returned responses to be the same as the order in which the requests were made. |
Lifecycle of a processor
When the World Modeler API receives a request to evaluate a DecisionModel for the first time, it creates a Processor instance that is then associated with the Decision Model for its entire lifetime. As with all other objects in World Modeler, a Processor is identified by its ID, a GUID that will not change for the life of the Processor instance. The mapping between the Processor and its Decision model is immutable; a single processor will always evaluate one and only one Decision Models (although multiple processors may be running evaluations of the same Decision Models in some circumstances). So the relationship between Decision Moldels and Processors in one-to-many.
The lifecyle of a Processor from creation to evaluating its decision model is shown below.
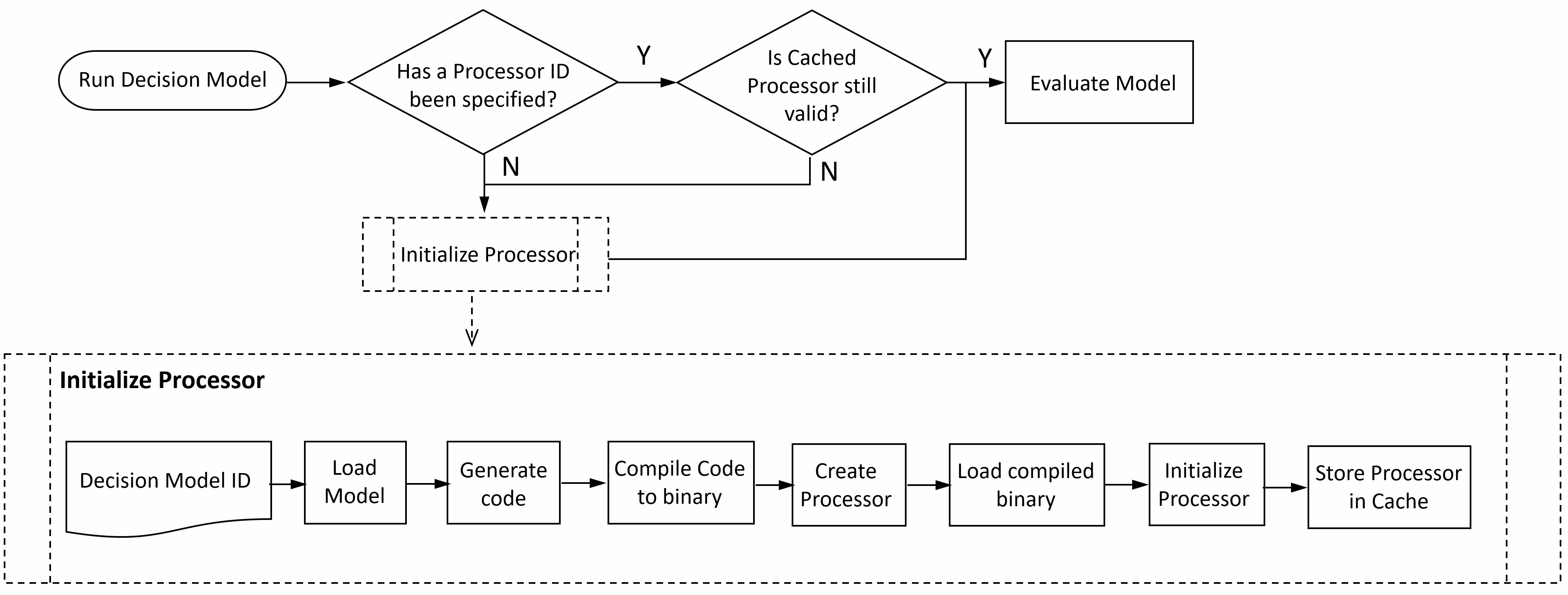
Before a Processor can be used, it must first be initialized. This is a relatively resource-intensive process as the Deicsion Model must be laoded (possibly from the database), source code generated from the model, the source code compiled to binary code, the Processor instance created, the binary code loaded into the Processor, and the Processor initialized. Ideally, this should only be done once, and once initialized, the Processor should be retained and service future requests to evaluate the decision model again with changes to the arguments. For this reason, when a new Processor is created, World Modeler Server stores it in a cache and retrieves it for futuer evaluation requests, using its ID as the cache key.
How the Procssor lifecycle affects API requests
The API Run operation is the primary means of invoking a processor. The interaction with the Processor lifecycle is primarkly via theprocessorID arguments and the value to which it is set. The normal protocol is as follows.
First time Run is called for a Decision Model: | The processorID arguments is set to null. This triggers
the initialization process shown in the above diagram, which is necessary to create and configure the Processor the first time it is used,
but only the first time.
When the first call to |
Subsequent calls to Run for the same Decision Model | In subsequent calls to Run, the processorID
should be set in the requerst body, as shown above. This will prevent re-initialization of a new Processor, will retrieve the
existing Processor from the cache, and evaluate the Decision Model with the specified arguments. |
Note that at any stage, calling
RunwithprocessorID = nullwill invalidate the current Processor and cause a new Processor instance to be created and initialized, following the process shown in the above diagram.Note that re-initializing the Processor will restore the model to its default state and previously calculated values will be reset.
Will a cached Processor always be available in the future?
No. There are two reasons an existing cached processor may "disappear".:- The cache timeout expires. This set set in the instance configuration of the World Modeler Server but is typically set to several hours or longer.
- The Decision Model associated with the cached Processor is changed. In this situation, the model must be re-loaded, re-compiled, and the Processor re-initialized.
Handling status code 410 (Gone)
If the ID of a Processor that was once available in the cache, but is no longer available, is used in a call toRun, the status code 410 (Gone)
is returned. The reason the Processor has been removed from the cache is also returned in the message field of the response.
If a 410 status code is returned as the response to a Run request, a new request should be sent to the Run API with processID = null
and the normal procedure followed after that.
Get(string)
Get the full details of the EvaluationEvaluation record with the specified ID.
Declaration
[HttpGet("evaluation/{id}")]
public string Get(string id)Parameters
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| string | id | ID of the Evaluation record |
Returns
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| string | The full details of the Evaluation record with the requested ID. |
GetAll(string)
Get the collection of all Evaluations associated with the specified DecisionModelDecisionModel.
Declaration
[HttpGet("evaluation/all/{decisionModelID}")]
public IEnumerable<string> GetAll(string decisionModelID)Parameters
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| string | decisionModelID | ID of the DecisionModel whose Evaluation records are to be retrieved. |
Returns
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| IEnumerable<string> | Collection of Evaluation records in short EvaluationDTO form |
Put(int, string)
Update the Evaluation record with the specified ID.
Declaration
[HttpPut("evaluation/{id}")]
public void Put(int id, string value)Parameters
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| int | id | ID of the Evaluation record to update. |
| string | value | Evaluation object containing the values to update. |